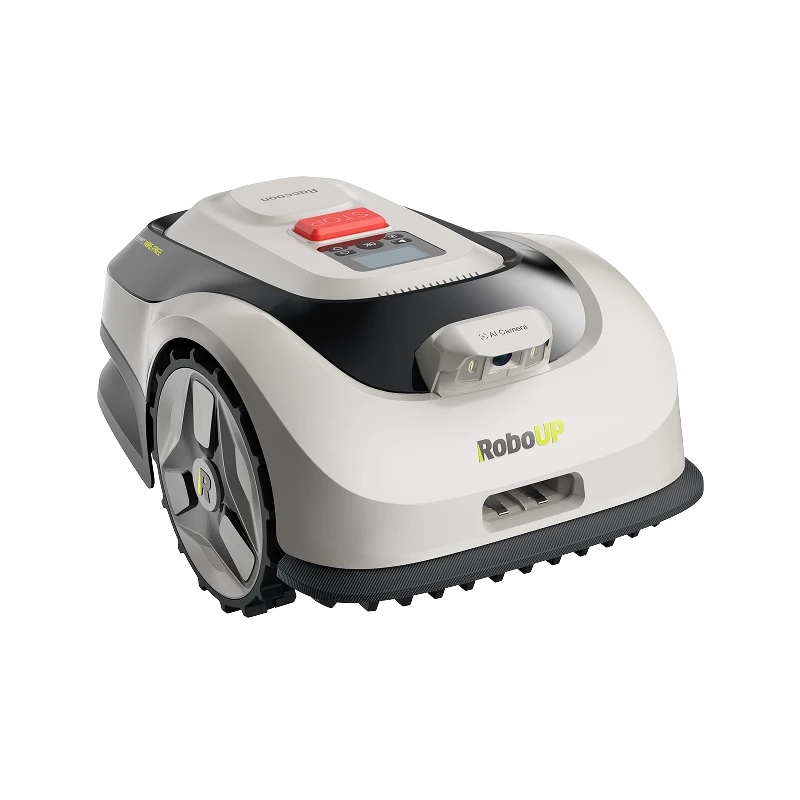
Precise Navigation: Exploring Mainstream Positioning Technologies with RoboUP
RoboUP - 2024/02/19
In the ever-evolving landscape of positioning technologies, the quest for precision, reliability, and adaptability has given rise to an array of cutting-edge solutions. This analysis delves into four distinct positioning technologies that have reshaped the realms of navigation, mapping, and environmental perception. These technologies are called Inertial Navigation System (INS), Real-Time Kinematic (RTK), Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), and Artificial Intelligence Vision (AI Vision). The philosophy at RoboUP underscores the belief that a singular technology may not fully address the diverse applications. Whether it's INS, RTK, LiDAR, or AI Vision, they all come with their unique strengths and limitations.
Inertial Navigation System (INS)
Cost: Low
Maturity: Moderate to High
With the development of global satellite navigation systems such as GPS and GLONASS, RTK, as a technology enhancing positioning accuracy, has been widely adopted, especially in surveying and precision agriculture.
Advantages:
Strong Autonomy: INS operates independently of external signals, functioning in diverse environments, including indoor, underground, or electronic interference zones.
High Privacy: As it does not rely on external signals, INS emits minimal radiation to external observations, safeguarding the privacy of missions.
Disadvantages:
Cumulative Errors: Over time, tiny errors in inertial components accumulate, gradually reducing the positioning accuracy after prolonged use.
Requires Initial Positioning Information: INS necessitates accurate initial positioning information during startup to ensure navigation precision.
RTK Real Time Kinematic Positioning Technology
Cost: Moderate
RTK systems require receivers and supporting software, and subscription services may be needed to access differential signals. However, compared to LiDAR, the overall cost of RTK systems is relatively lower.
Maturity: Moderate to High
With the development of global satellite navigation systems such as GPS and GLONASS, RTK, as a technology enhancing positioning accuracy, has been widely adopted, especially in surveying and precision agriculture.
Advantages:
High Precision: RTK can provide centimeter-level positioning accuracy, making it suitable for applications that demand high-precision navigation.
Real-Time Capability: RTK offers real-time positioning data, making it well-suited for precise navigation in dynamic environments.
Disadvantages:
Signal Dependency: RTK relies on global satellite navigation systems, so it may not function in environments with weak or no signals.
Electromagnetic Interference: The performance of RTK may be affected in the presence of strong electromagnetic interference.
LiDAR
Cost: High
The cost of LiDAR systems depends on their accuracy and complexity, with high-end systems being expensive, especially those used for autonomous driving.
Maturity: Moderate to High
LiDAR technology is becoming increasingly popular in the fields of autonomous vehicles and robotics. While its fundamental principles have been around for some time, its application as a mainstream commercial positioning solution is relatively new.
Advantages:
High Precision Measurement: LiDAR, through high-precision laser ranging, it can accurately measure the distance of objects in the environment.
Environmental Modeling: It can create high-resolution environmental map models, facilitating precise navigation and obstacle avoidance for robotics.
Disadvantages:
Limitations in Object Recognition: Despite LiDAR's accurate distance measurement capabilities, it cannot identify the types of objects, limiting its strategic obstacle avoidance abilities in complex environments.
Detection Range Limitations: The detection range of LiDAR is constrained by its technology and design, potentially not covering all areas within the environment.
AI Vision
Cost: Moderate
The development and implementation of AI Vision systems require significant investments in both hardware, such as high-performance cameras and processing units, and software, including complex machine learning models. Additionally, there are ongoing costs associated with data training and optimization.
Maturity: Moderate to Low
AI Vision is a rapidly advancing field. While the underlying visual processing and recognition technologies are not new, integrating AI into advanced environmental perception and navigation systems is a recent development. These systems are still undergoing continuous research and improvement.
Advantages:
Environmental Perception: By simulating human vision, AI vision systems can recognize and understand the surrounding environment, providing rich navigation information.
Versatility: With the integration of cameras and multi-vision systems, AI vision doesn't just measure the distance but also performs complex environmental recognition and classification tasks.
Disadvantages:
Dependency on Lighting Conditions: The performance of AI vision systems is significantly reliant on environmental lighting conditions. Insufficient or excessive lighting can potentially impact its functionality.
High Processing Complexity: Processing and analyzing visual data demand high computational power, potentially leading to increased system complexity and extended response times.
RoboUP advanced navigation lawn mower ready for the intricate challenges in achieving precise positioning, has been at the forefront of technology integration by combining RTK, vSLAM, INS, and AI Vision. We aim to unravel the intricacies of these positioning technologies, explore their applications, and provide users with an adaptive approach to positioning systems that lead to better navigation.
Beyond Boundaries: RoboUP's Quest for Innovation in Robot Lawn Mowers RoboUP T1200 Pro: Enhancing Positioning for Exceptional Performance