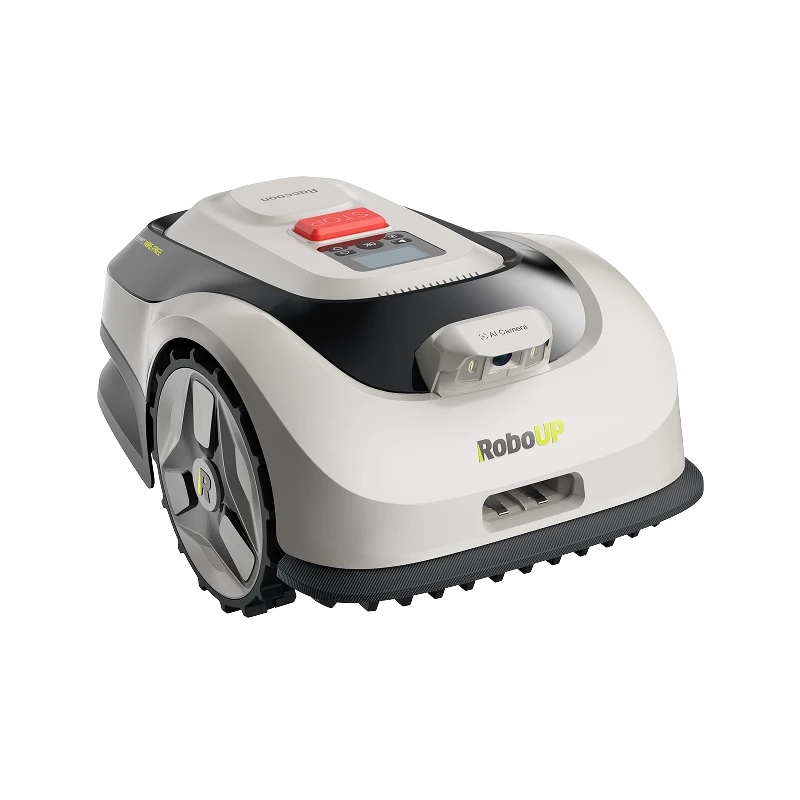
INS (Inertial Navigation System)
An INS (Inertial Navigation System) consists of the IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) and the odometer (distance meter). The data from the gyroscope, accelerometer and distance meter can be used to calculate the relative position, orientation and attitude of RoboUP. The accuracy of the INS is not reliant on a clear view of the satellite, which aids in precise navigation in challenging garden conditions, such as areas under trees or roof extensions.
Advantages:
INS operates independently of external signals, functioning in diverse environments, including indoor, underground, or electronic interference zones. As it does not rely on external signals, INS emits minimal radiation to external observations, safeguarding the privacy of missions.
Disadvantages:
Over time, the tiny errors in inertial components accumulate, gradually reducing the positioning accuracy after prolonged use. INS necessitates accurate initial positioning information during startup to ensure navigation precision.